Hello all.
With an engine-less and transmission-less base-car-structure having in each wheel a, say, 20kW electric motor and the wiring / circuitry to a central box, various electric cars could be made.
With a lot of batteries somewhere in the car, the base-car-structure turns to a plug-in electric.
With batteries and a small REM (Range Extender Module) it turns to a plug-in electric wherein a small internal combustion engine is used in emergency (say, when the battery is empty).
With fewer batteries and a bigger REM, the car is less plug-in and more internal-combustion-engine dependent.
Without batteries, but with a big REM, the car is closer to a conventional car but rid of gearbox, of transmission, of differentials, of drive shafts, of CVJ’s etc.
A control box / program is the mind / brain of the car.
Reasonably, soon the carmakers will provide such base-car-structures. Initially the customer will have to pick his desirable battery pack and his desirable REM from the same carmaker.
Latter, the carmakers will agree to make compatible base-car-structures so that the customer will be able to combine any compatible battery pack and any compatible REM from the market with his base-car-structure.
Say like what happens with the Desktop computers wherein the customer picks his favorite compatible subunits (video card, DVD, hard disk etc) to complete the basic structure.
It seems that the REM’s will become more and more important in the auto industry.
The REM will be the heart of the car.
The REM comprises one or more electric generators and an internal combustion engine driving the electric generator(s).
The characteristics and design of the internal combustion engine of a REM are substantially different than those of a conventional internal combustion engine of a car.
For instance,
think of a substantially over-square design (like, say, the Ducati Panigale 1299: 60.8mm stroke, 116mm bore) wherein the crankshaft is small relative to the cylinder head.
What if instead of combining two big cylinder heads with a common (and compact) crankshaft / crankcase (as happens in the Ducati Panigale), a unique cylinder head were combined with two crankshafts?
Here is a 4-stroke even-firing Opposed-Piston PatRoVa rotary valve engine, wherein a unique rotary valve serves two cylinders:
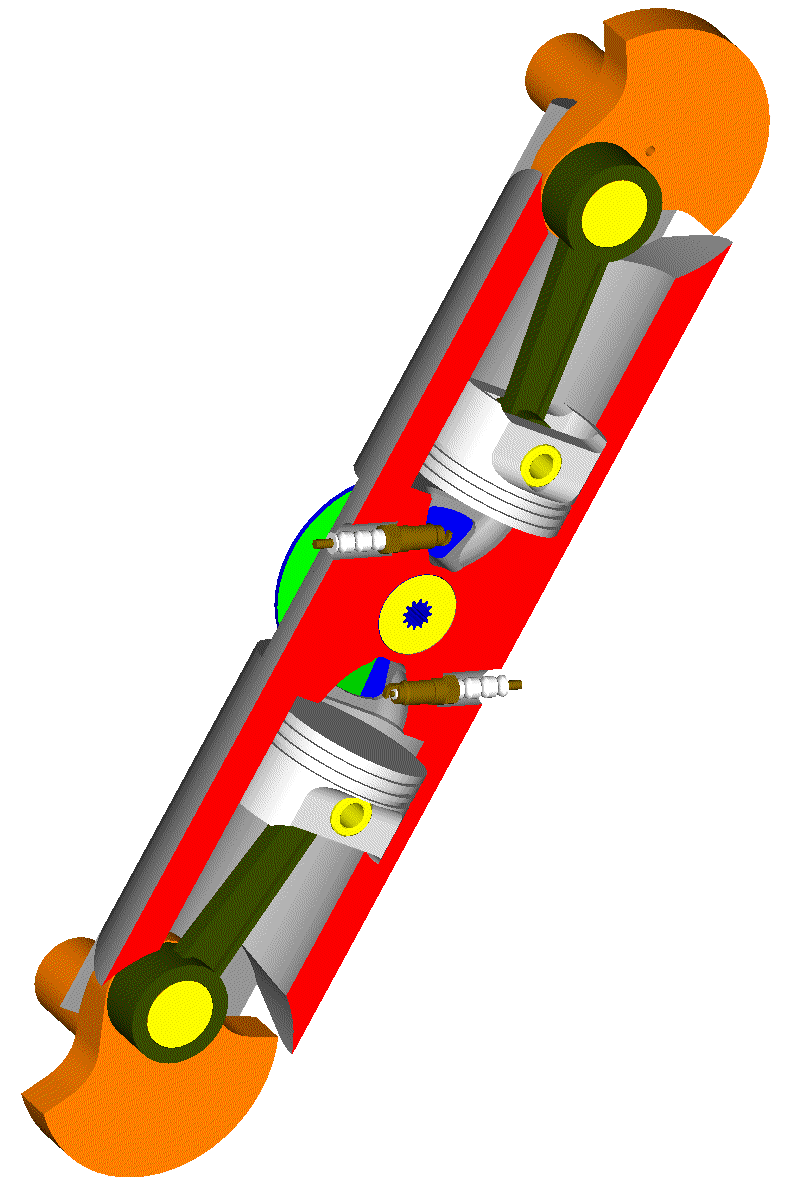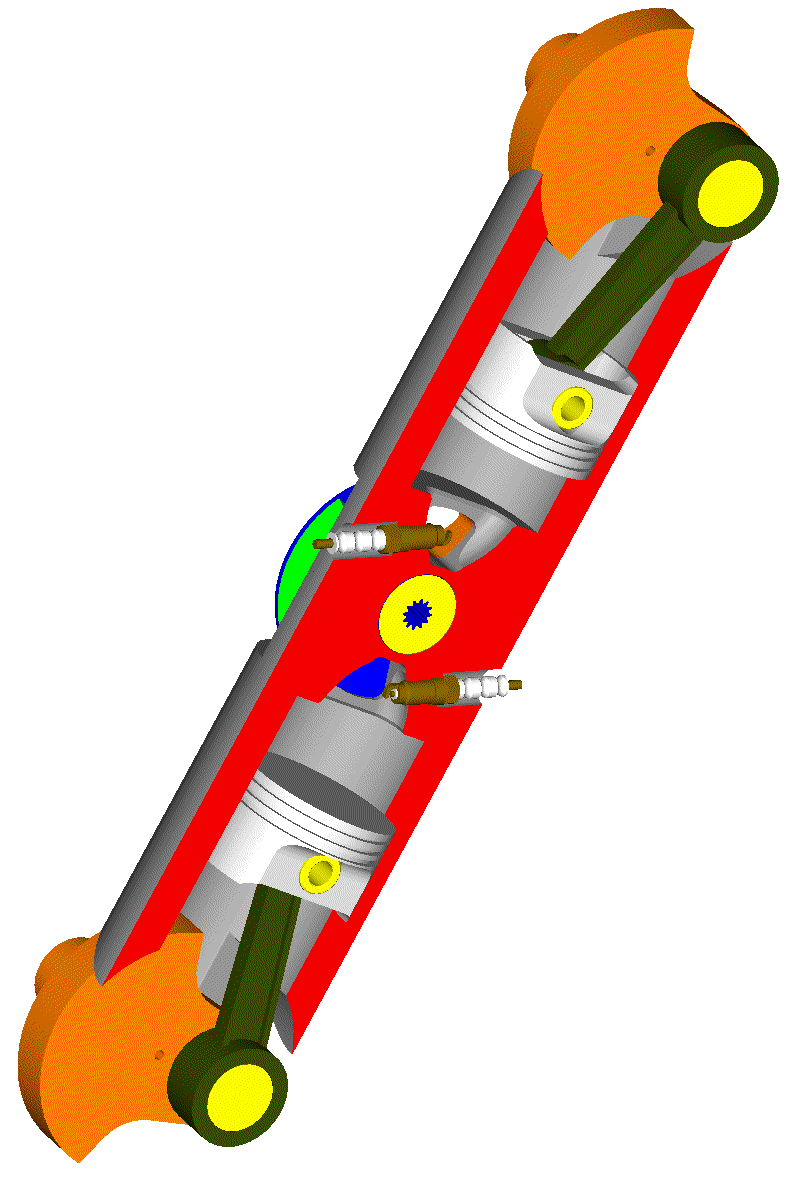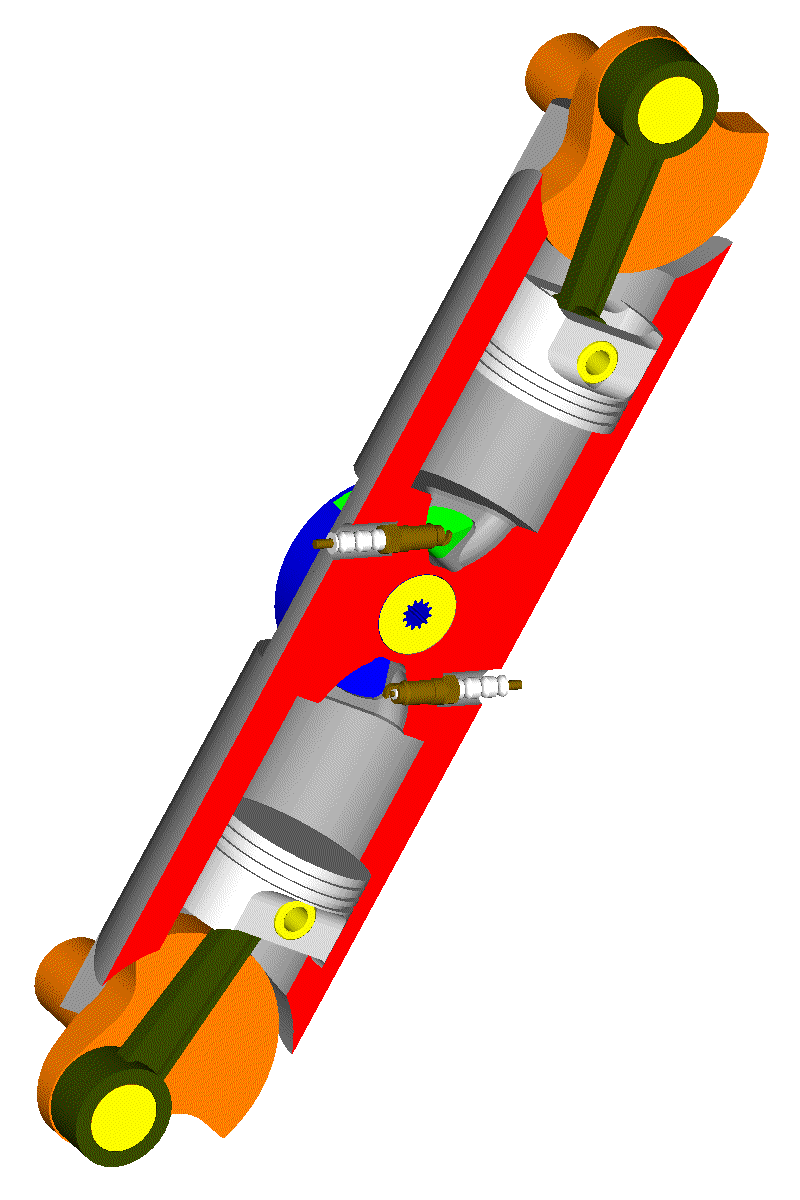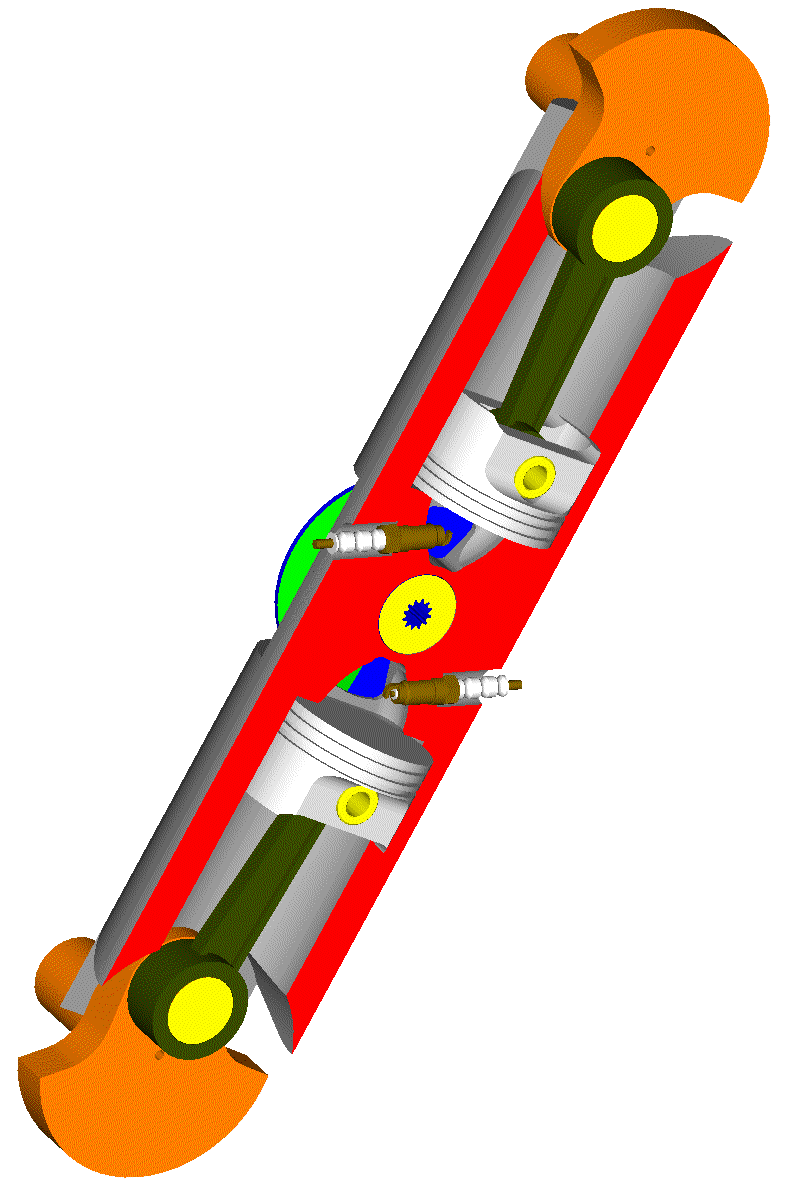
Think of a REM having an electric generator at each crankshaft of the above engine.
Or think of the balancing / vibration-free-quality of such a solution (perfectly balanced).
Or think how much the crankshaft balance webs can be reduced without affecting the balancing quality.
Or think about the NVH properties of such a unit; without poppet valves to hit on their seats, the engine runs quieter; without free inertia vibrations the engine runs smoother; without combustion vibrations the overall NVH improves.
Or think how much simpler the intake and exhaust plenums can be made. Etc.
Thanks
Manolis Pattakos




















